Welcome to the fascinating world of monkeys, where diversity reigns supreme! These playful and curious creatures have captured our hearts with their charming antics and intriguing behaviors. From the treetops of lush rainforests to the vast savannas, monkeys have established their presence across diverse habitats, adapting to each environment in unique ways.
In this exploration of “Types of Monkeys,” we’ll embark on a journey to discover the rich tapestry of primate life. From the acrobatic agility of the spider monkey to the endearing social dynamics of the capuchin, we’ll delve into the remarkable traits that set each monkey species apart. Whether you’re a wildlife enthusiast or simply curious about these intelligent beings, join us as we unravel the secrets of the monkey world, uncovering the various species, their habitats, and the remarkable roles they play in the ecosystems they call home. Get ready to meet our primate cousins, and prepare to be enchanted by the captivating world of monkeys!
Different Types Of Monkeys
Chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes) – Our Intelligent Kin:
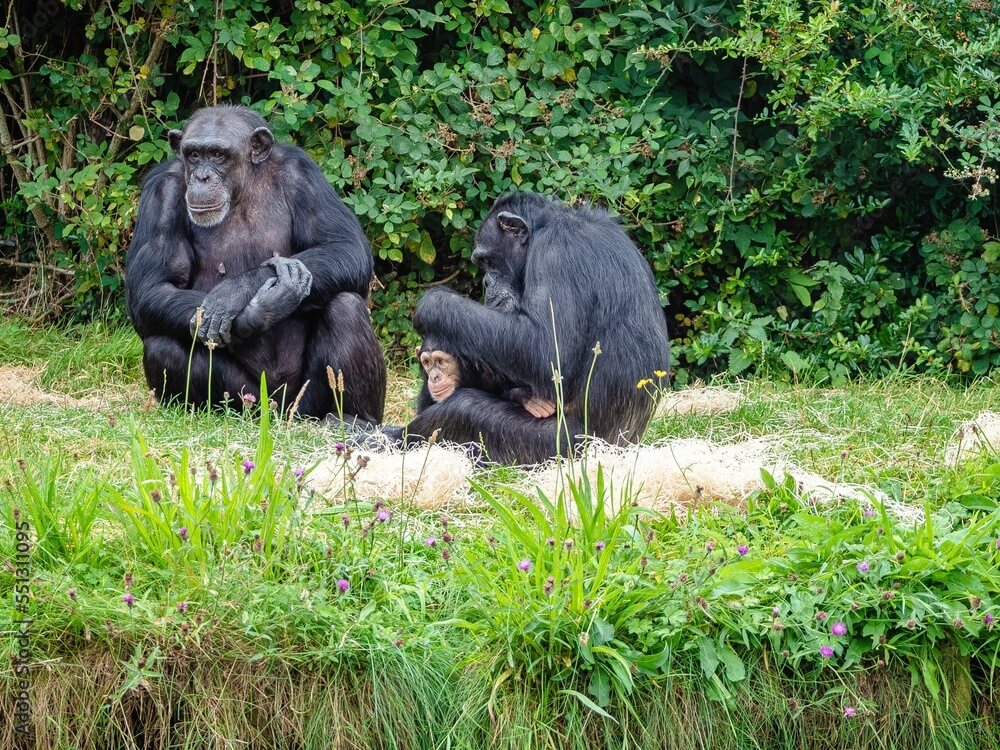

Scientific Name: Pan troglodytes
Where Found: Chimpanzees are primarily found in the forests and woodlands of central and western Africa, spanning across countries such as Cameroon, Uganda, the Democratic Republic of Congo, and more.
Places to See: If you’re eager to observe chimpanzees in the wild, the Mahale Mountains National Park in Tanzania offers a unique opportunity. This park is home to one of the largest chimpanzee populations and offers a chance to witness their intricate social behaviors in a breathtaking natural setting. Additionally, Gombe Stream National Park in Tanzania, where Jane Goodall conducted her groundbreaking research, provides an unforgettable experience to encounter these remarkable creatures up close.
Detailed Explanation:
Chimpanzees are often considered our closest living relatives, sharing approximately 98% of their DNA with humans. Inhabiting the dense forests of Africa, they showcase intricate behaviors and social structures that captivate researchers and enthusiasts alike. Chimpanzees live in communities where strong relationships and hierarchies shape their interactions.
Behavior and Social Structure: Chimpanzees exhibit complex behaviors, using vocalizations, body language, and facial expressions to communicate within their tight-knit communities. Their intelligence is evident in their ability to use tools, such as sticks and leaves, to extract termites and nuts for consumption. This behavior varies among different communities, showcasing their cultural diversity.
Physical Traits: These primates have coarse black hair covering their bodies, with bare faces, ears, fingers, and toes. Their long arms and brachiating abilities enable them to swing through trees effortlessly. Males stand at about 4 to 5.6 feet (1.2 to 1.7 meters) and weigh around 90 to 120 pounds (40 to 54 kilograms), while females are slightly smaller.
Diet and Habits: Chimpanzees are omnivores, relishing fruits, plants, insects, and occasionally small animals. Their social grooming practices strengthen bonds within the community. They engage in playful behaviors, showing their emotional depth and ability to adapt to changing circumstances.
Conservation: Unfortunately, chimpanzees face grave threats including habitat loss, hunting, and disease. Organizations are dedicated to preserving their habitats and raising awareness about their importance in the ecosystem.
Howler Monkeys (Genus: Alouatta) – Serenading the Canopy:
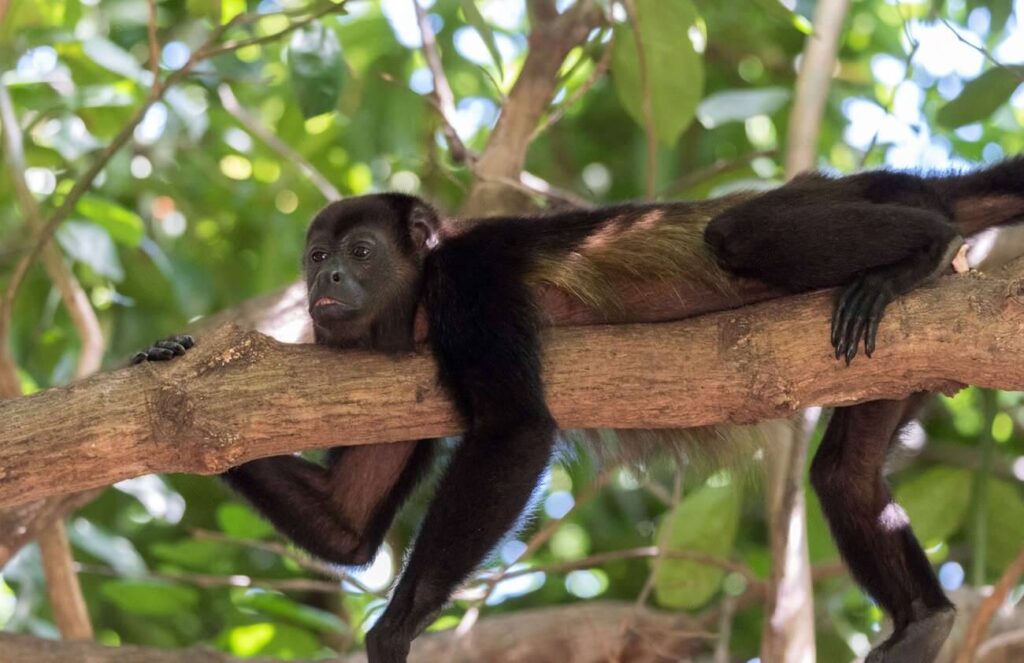

Scientific Name: Genus: Alouatta
Where Found: Howler monkeys thrive in the rainforests of Central and South America, spanning countries like Brazil, Mexico, Costa Rica, and Venezuela.
Places to See: For an incredible experience with howler monkeys, consider visiting the Osa Peninsula in Costa Rica. Corcovado National Park, located here, is a prime spot for observing these primates in their natural habitat. The Amazon Rainforest in Brazil and Tambopata National Reserve in Peru also offer opportunities to encounter howler monkeys and appreciate their crucial role in the rainforest ecosystem.
Detailed Explanation:
Howler monkeys, known for their distinctive vocalizations, play a vital role in the ecosystem of their lush rainforest homes. These primates are fascinating not only for their unique communication but also for their arboreal lifestyle and contributions to the natural world.
Vocal Communication: Howler monkeys are famous for their resounding calls that echo through the forest canopy. Their calls serve multiple purposes, including establishing territory and maintaining troop cohesion. These vocalizations, which can travel up to three miles, are among the loudest in the animal kingdom.
Diet and Physical Traits: These herbivorous monkeys consume leaves, fruits, flowers, and occasionally insects. Their prehensile tails aid in navigating their treetop environment, allowing them to grasp branches securely. Howler monkeys come in various sizes, with males generally larger than females. Their fur color ranges from shades of brown to black.
Conservation Efforts: While some howler monkey species are classified as least concern, habitat destruction due to deforestation threatens others. Conservation initiatives that protect tropical forests indirectly contribute to the preservation of howler monkey populations by ensuring their habitats remain intact.
Understanding the lives, behaviors, and roles of chimpanzees and howler monkeys in their respective ecosystems offers a glimpse into the intricate tapestry of the natural world. These fascinating primate species serve as a reminder of our interconnectedness with the animal kingdom and the importance of safeguarding their habitats for generations to come.
Spider Monkey (Genus: Ateles) – Agile Canopy Dwellers:
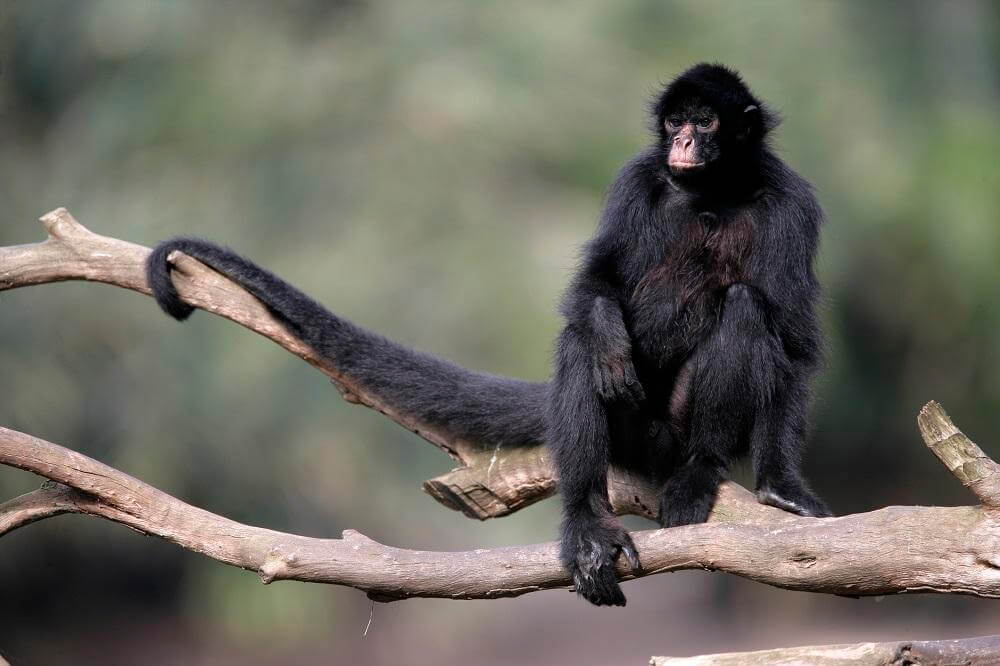

Scientific Name: Genus: Ateles
Where Found: Spider monkeys inhabit the tropical forests of Central and South America, ranging from Mexico to Brazil, including countries like Costa Rica, Panama, and Venezuela.
Places to See: One of the ideal places to observe spider monkeys is the Osa Peninsula in Costa Rica. Corcovado National Park, part of this region, offers opportunities to witness these acrobatic primates swinging through the treetops. Additionally, Manu National Park in Peru is another fantastic destination for encountering spider monkeys in their natural habitat, especially within the lush Amazon rainforest.
Detailed Explanation:
Spider monkeys, with their long, slender limbs, are incredibly agile and skilled at traversing the forest canopy. Their prehensile tails act as an extra limb, allowing them to move effortlessly among the trees. These monkeys are a captivating sight in their natural habitat, contributing to the biodiversity of their ecosystems.
Behavior and Social Structure: Spider monkeys are social animals, often found in groups known as troops. These troops can consist of several individuals, fostering social bonds through grooming and playful interactions. They primarily consume fruits, leaves, flowers, and occasionally insects, making them essential seed dispersers in the forest.
Physical Traits: With a slender body covered in dark fur, spider monkeys have a unique feature—a prehensile tail that acts as a fifth hand, providing exceptional grip and support while swinging or reaching for food. Their arms are longer than their legs, suited for life in the trees, and they have distinctive, expressive faces.
Conservation Status: Spider monkeys face threats from habitat loss due to deforestation and the illegal pet trade.
Capuchin Monkey (Genus: Cebus) – Adaptable and Clever:
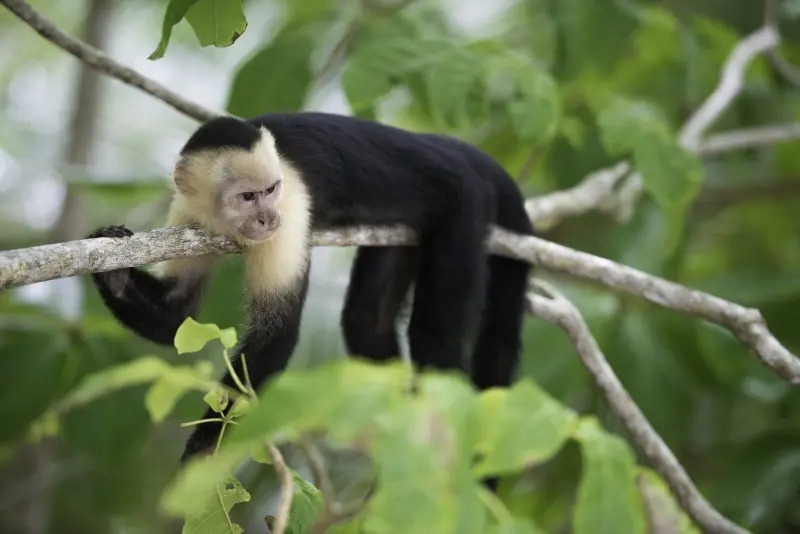

Scientific Name: Genus: Cebus
Where Found: Capuchin monkeys have a broad distribution across Central and South America, inhabiting diverse environments from tropical rainforests to dry woodlands. They can be found in countries like Brazil, Costa Rica, Panama, and Colombia.
Places to See: The Manuel Antonio National Park in Costa Rica is a popular destination to see capuchin monkeys. Their curious nature often leads them to interact with visitors, providing an excellent opportunity for observing these intelligent primates. Additionally, the Amazon Rainforest in Brazil and the Osa Peninsula in Costa Rica offer chances to encounter capuchin monkeys.
Detailed Explanation:
Capuchin monkeys, recognizable by their small size and distinctive face, are highly intelligent and adaptive creatures. They have been known to use tools, a behavior that has fascinated researchers studying their cognitive abilities.
Behavior and Social Structure: Capuchin monkeys are social animals, living in groups called troops. They are highly skilled at foraging, using their dexterous hands and sharp intelligence to find a variety of food, including fruits, insects, and even small vertebrates.
Physical Traits: Capuchins have a robust body covered in fur, with a distinct lighter-colored face, giving them a unique appearance. They are agile climbers and are known for their ability to leap between trees, showing off their impressive agility.
Conservation Status: While not as threatened as some other monkey species, capuchin monkeys face habitat fragmentation due to deforestation. Conservation efforts aim to protect their habitats and ensure these fascinating primates continue to thrive.
These four types of monkeys, including chimpanzees, howler monkeys, spider monkeys, and capuchin monkeys, provide a glimpse into the incredible diversity of primates across different regions, demonstrating the importance of conservation and appreciation for the natural world.
Gibbons (Family: Hylobatidae) – Melodious Tree Swingers:
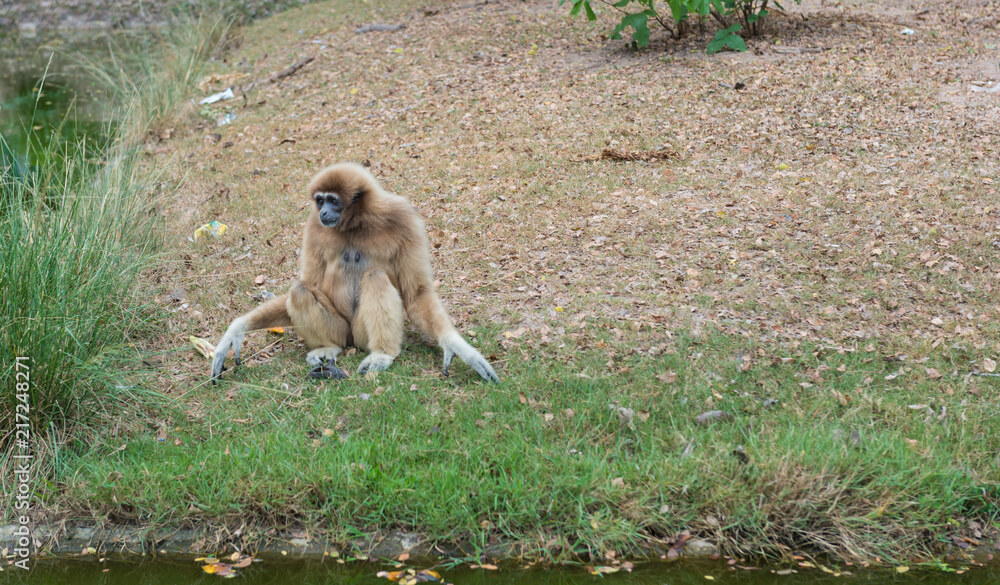

Scientific Name: Family: Hylobatidae (includes various genera such as Hylobates, Nomascus, and others)
Where Found: Gibbons are primarily found in the tropical and subtropical rainforests of Southeast Asia, including countries such as Thailand, Indonesia, Malaysia, Laos, and Vietnam.
Places to See: The dense forests of Borneo, particularly Gunung Palung National Park in Indonesia, offer opportunities to witness the graceful and agile gibbons swinging through the treetops. Additionally, the Phuket Gibbon Rehabilitation Project in Thailand allows visitors to observe rescued gibbons and learn about their conservation.
Detailed Explanation:
Gibbons are known for their incredible agility and melodious calls that resonate through the forest. These small to medium-sized apes are primarily arboreal, spending their lives in the treetops where they swing effortlessly between branches, demonstrating their remarkable adaptation to life in the canopy.
Behavior and Social Structure: Gibbons live in small family groups and are monogamous, forming strong bonds with their mates. They are diurnal, meaning they are active during the day, and their long arms, along with their hook-like hands, make them exceptional brachiators.
Physical Traits: Gibbons have a slender, lightweight body, covered in fur that can range in color from black to various shades of brown and even white in some species. They have a distinct throat sac that amplifies their vocalizations, allowing them to communicate across the forest.
Conservation Status: Gibbons face threats from habitat loss due to deforestation and the illegal pet trade. Conservation efforts aim to protect their habitats and raise awareness about the importance of preserving these acrobatic and melodious primates.
Mandrills (Mandrillus sphinx) – Colorful Rainforest Royalty:
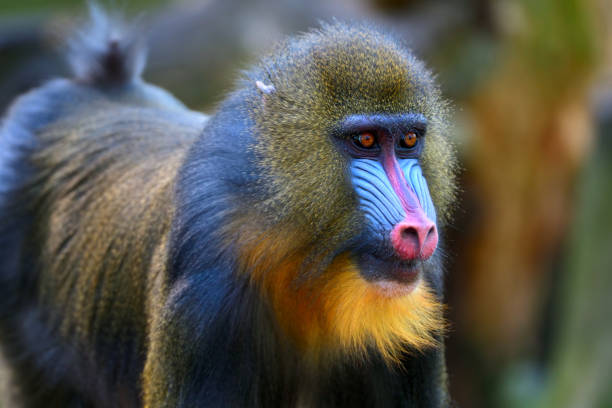

Scientific Name: Mandrillus sphinx
Where Found: Mandrills are found in the rainforests of central and western Africa, primarily in countries such as Cameroon, Gabon, Equatorial Guinea, and the Congo Basin.
Places to See: The Lopé National Park in Gabon is known for its mandrill population, offering a chance to see these vibrant monkeys in their natural habitat.
Detailed Explanation:
Mandrills are the largest of all monkeys and are instantly recognizable by their colorful faces, making them an iconic species in the African rainforest. These primates are known for their striking appearance and complex social behavior.
Behavior and Social Structure: Mandrills live in large, mixed-gender groups known as hordes, which can consist of hundreds of individuals. These hordes have a hierarchical structure, with dominant males leading the group.
Physical Traits: Mandrills are easily identified by the vivid colors on their faces, which vary with age, gender, and social status. Males have bright blue and red coloring on their noses, while females and lower-ranking males display more subdued hues. They have a stocky build and powerful jaw, allowing them to consume a varied diet of fruits, insects, and even small vertebrates.
Conservation Status: Mandrills face threats from habitat loss due to deforestation and hunting. Conservation efforts are focused on protecting their habitats and promoting sustainable practices to ensure the survival of these majestic and colorful rainforest inhabitants.
These additional monkey species, including gibbons and mandrills, showcase the incredible diversity of primates across different regions, emphasizing the need for conservation and admiration for the fascinating natural world.
Golden Lion Tamarin (Leontopithecus rosalia) – A Glimpse of Gold in Brazil’s Rainforests:

Scientific Name: Leontopithecus rosalia
Where Found: Golden lion tamarins are endemic to the Atlantic coastal forests of Brazil. Their range includes the states of Rio de Janeiro and São Paulo.
Places to See: The Poço das Antas Biological Reserve, located in the state of Rio de Janeiro, is a significant protected area for golden lion tamarins. This reserve offers opportunities to witness these stunning primates in their natural habitat. Additionally, various conservation programs and eco-tourism initiatives in Brazil focus on preserving these endangered tamarins, providing visitors with a chance to observe them while contributing to their conservation.
Detailed Explanation:
The golden lion tamarin, with its vibrant reddish-gold fur and distinctive manes, is a captivating and critically endangered species. This small primate holds a special place in the biodiversity of the Brazilian rainforests.
Behavior and Social Structure: Golden lion tamarins are highly social animals, living in family groups that usually consist of a breeding pair and their offspring. They communicate through a range of vocalizations, which help coordinate activities within the group and maintain territorial boundaries.
Physical Traits: Their golden fur, especially the mane around their faces, makes them stand out in the lush green rainforest. They have a compact body, with long limbs and a prehensile tail, which allows them to move nimbly through the treetops.
Diet and Conservation: These tamarins primarily feed on fruits, insects, and small vertebrates. They face significant threats due to habitat loss from deforestation, and they are also impacted by illegal pet trade. Conservation organizations in Brazil work diligently to protect their remaining habitat and raise awareness about the importance of safeguarding these beautiful primates.
Japanese Macaque (Macaca fuscata) – Snow Monkeys of Japan:
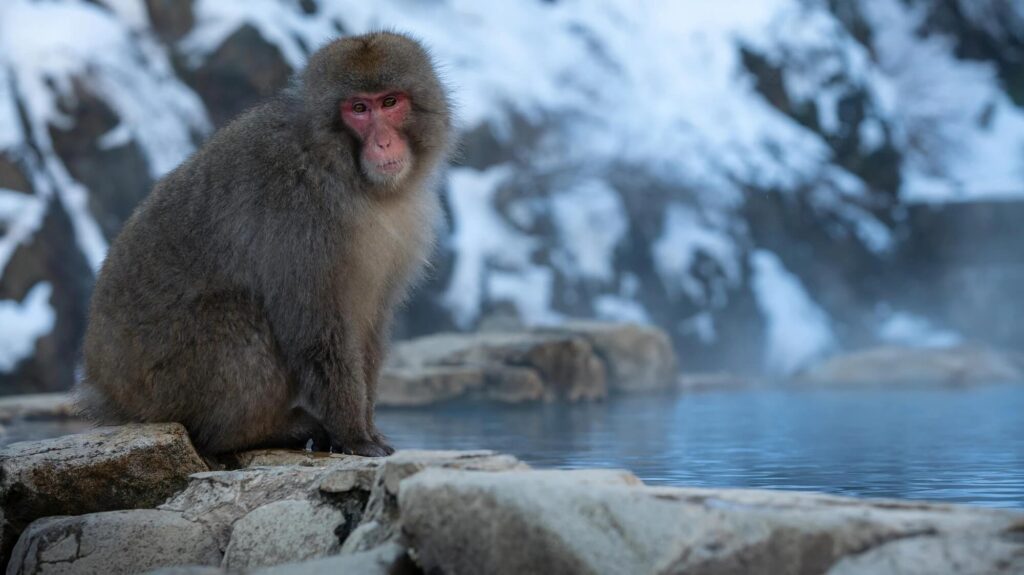

Scientific Name: Macaca fuscata
Where Found: Japanese macaques are native to various regions of Japan, including the Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu islands. They are known to inhabit forests and mountainous areas.
Places to See: The Jigokudani Monkey Park in Nagano Prefecture, Japan, is famous for its hot springs where Japanese macaques often come to bathe during the winter months. This unique behavior has earned them the nickname “snow monkeys.” Observing them in the snow-covered landscape is a popular attraction for tourists interested in wildlife and nature.
Detailed Explanation:
Japanese macaques, often referred to as snow monkeys due to their ability to endure cold climates, are a culturally significant and iconic species in Japan.
Behavior and Social Structure: Japanese macaques live in multi-generational groups, exhibiting a complex social hierarchy. They are known for their fascinating behavior of using natural hot springs to keep warm during the winter, a behavior that has been observed primarily in the Jigokudani Monkey Park.
Physical Traits: Their fur varies in color from brown to grey, with a distinct pinkish-red face. Their fur becomes thicker in the winter months to help them withstand the colder temperatures.
Diet and Conservation: Japanese macaques are omnivores, consuming a variety of foods, including fruits, vegetables, insects, and even small vertebrates. While they are not currently considered endangered, conservation efforts in Japan aim to protect their habitats and ensure that they coexist harmoniously with local communities.
These additional monkey species, including golden lion tamarins and Japanese macaques, add to the rich diversity of primates worldwide, highlighting the importance of conservation and the enchanting allure of observing these captivating creatures in their natural environments.
Tarsiers (Family: Tarsiidae) – The Nighttime Hunters with Enormous Eyes:
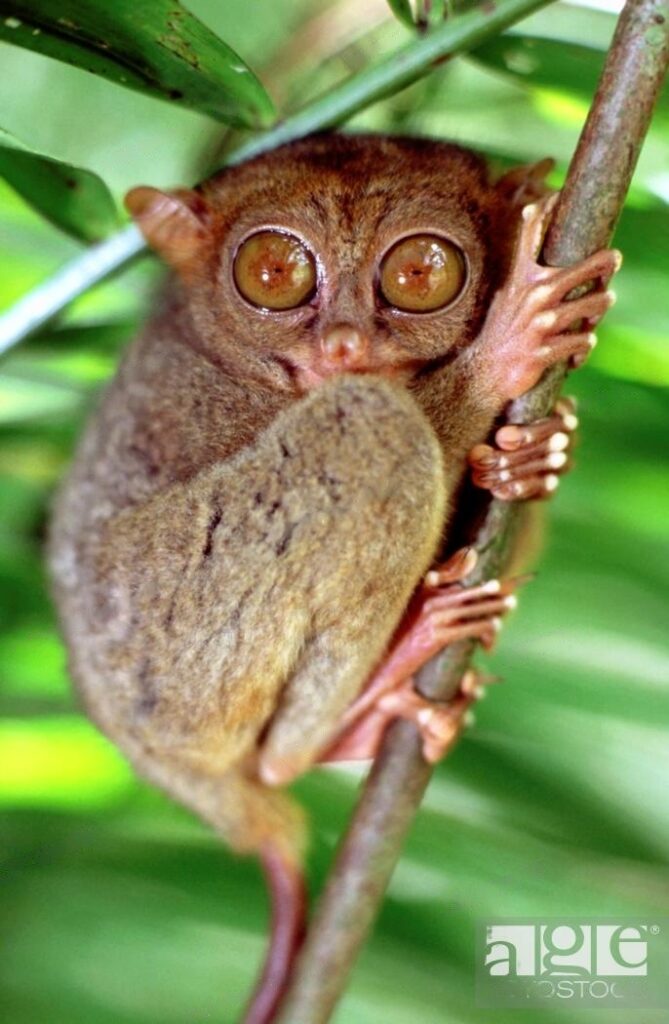

Scientific Name: Family: Tarsiidae (includes various genera such as Tarsius)
Where Found: Tarsiers are found in Southeast Asia, including countries such as the Philippines, Indonesia, Malaysia, and Borneo.
Detailed Explanation:
Tarsiers are unique and fascinating primates known for their enormous eyes, specialized adaptations for nocturnal hunting, and distinctive features that set them apart from other primates.
Behavior and Social Structure: Tarsiers are solitary and primarily nocturnal, feeding on insects and small vertebrates under the cover of darkness. Their enormous eyes help them capture prey in low-light conditions.
Physical Traits: Tarsiers have large eyes that enable exceptional night vision, as well as a unique feature called the “tarsus,” an elongated ankle bone that allows them to make remarkable leaps from tree to tree. Their large eyes give them a distinctive appearance and enhance their ability to locate prey.
Conservation Status: Some tarsier species are currently listed as vulnerable due to habitat loss, deforestation, and illegal pet trade. Conservation efforts focus on protecting their habitats and raising awareness about their importance in maintaining the balance of ecosystems in Southeast Asia.
These two unique monkey species, snow monkeys and tarsiers, contribute to the diverse array of primates across different regions, highlighting the importance of preserving their habitats and appreciating the wonders of the natural world.
Proboscis Monkey (Nasalis larvatus) – Quirky Residents of Borneo:

Scientific Name: Nasalis larvatus
Where Found: Proboscis monkeys are endemic to the island of Borneo, specifically found in the coastal and mangrove forests of Malaysia (Borneo) and Indonesia (Kalimantan).
Places to See: To observe proboscis monkeys in their natural habitat, visiting the Kinabatangan River in Sabah, Malaysia, is an excellent choice. The river cruises offer opportunities to see these unique primates along with a variety of other wildlife in the lush Bornean rainforest.
Detailed Explanation:
Proboscis monkeys, with their distinctive large noses and unique appearance, are one of the quirkiest residents of the Bornean rainforest.
Behavior and Social Structure: Proboscis monkeys live in groups known as troops, typically consisting of several adult females and their offspring, along with a dominant male. These monkeys are excellent swimmers and are often seen near water bodies such as rivers and mangroves.
Physical Traits: The most prominent feature of probosci’s monkeys is their long, fleshy nose, which serves as a resonating chamber for their distinctive vocalizations. Males tend to have larger noses than females, and the size of the nose can vary among individuals. They have a pot-bellied appearance, with a reddish-brown coat and a distinctive pot-belly shape.
Diet and Conservation: Proboscis monkeys are primarily herbivores, consuming leaves, fruits, and flowers. They have a specialized stomach to digest their fibrous diet. Habitat loss due to deforestation and coastal development poses significant threats to their survival. Conservation efforts are focused on protecting their habitats and raising awareness about the importance of conserving Borneo’s unique biodiversity.
These additional monkey species, including mandrills and probosci’s monkeys, continue to illustrate the incredible diversity of primates across various regions, emphasizing the significance of conservation and the fascination of observing these remarkable creatures in their natural environments.
Must Read:-
- Top 10 Most Dangerous Animals in the World
- [Top 10] Most Stunning Fish in the World
- [Top 10] Zoo in America Uncovered
- Top 10 Cutest Animals In The World
Conclusion
In conclusion, the world of monkeys is a diverse and captivating one, encompassing a wide range of species with unique characteristics and habitats. From the intelligent and socially intricate chimpanzees to the melodious howler monkeys, the agile spider monkeys, the clever capuchins, the colorful mandrills, the enigmatic gibbons, the vibrant golden lion tamarins, the iconic Japanese macaques, the rainforest royalty of mandrills, and the quirky proboscis monkeys, each type of monkey plays a vital role in its ecosystem.
As we marvel at their beauty and behavior, it is crucial to recognize the importance of conservation efforts to preserve these fascinating creatures and the rich biodiversity they contribute to our planet.